Custom ERP Integration Guide
Automatically synchronize data between IrisX and ERP systems to maintain up-to-date information across platforms.
By following this guide, you will:
✔️ Understand how to authenticate and make requests to Iris Trackunit APIs.
✔️ Learn how to fetch asset details, locations, and operating hours from Trackunit.
✔️ Learn how to map and synchronize rental ERP data into Trackunit.
API authentication and setup process
Before you can start fetching data from or synching data to Trackunit Iris APIs, you need to authenticate your requests. The API uses OAuth 2.0 for secure access, ensuring that only authorized users and applications can retrieve asset data.
To obtain API credentials ask the Trackunit account owner to follow our Access Token guide to obtain OAuth 2.0 client credentials from the Manager application. Then your client application requests an access token from the IRIS Authorization Server, extracts a token from the response, and sends the token to the IRIS API that you want to access.
Get telematics data from Trackunit into an ERP system
The ISO Export API from Trackunit is a powerful tool that allows users to extract key telematics data from their fleet. It provides structured data export capabilities, enabling access to critical information such as:
- Asset details – Unique identifiers and metadata.
- Location data – GPS coordinates.
- Meter reading data – Total operating hours of assets.
Step 1: Fetching Asset Details, Locations, and Operating Hours
Once authenticated, you can retrieve asset information, including asset metadata, location data, and total operating hours. The ISO Export API provides structured endpoints to access this data efficiently.
Identifying assets
Across the ISO Export API endpoints all assets are identified via the so-called OEM ISO identifier (PIN or VIN). PIN is used for earth-moving machinery and may be used for other types of off-road machines. VIN is used for on-road vehicles. However both PIN and VIN are generally 17-character fields and either one is acceptable depending upon the classification of the specific machine. PIN is the name generally used to represent both. NOTE: Users are able to modify the field Serial Number (VIN) inside Trackunit, so the format and length might vary.
Retrieve data for the whole fleet / all assets
The fleet snapshot endpoint provides the snapshot of the latest available telematics data for all assets in the fleet:
- Asset meta data via the EquipmentHeader: Header information (EquipmentHeader) consists of Telematics Unit Installation Date (UnitInstallDateTime), Equipment Make (OEMName), Equipment Model (Model), Equipment ID (EquipmentID), Serial Number (SerialNumber) and OEM ISO Number (PIN). NOTE: PIN and VIN are generally both 17-character fields, but can be edited by users inside Trackunit which can cause the format and length to vary. Either PIN or VIN is acceptable depending upon the classification of the specific machine. PIN is the name used in to represent both.
- Location: The last known equipment location is expressed by the following fields: Date and time (DateTime), Latitude of location (Latitude), Longitude of location (Longitude), Altitude of location (Altitude) and Units of Altitude (AltitudeUnits).
- Meter readings via CumulativeOperatingHours: The current total lifetime operating hours of the machine is expressed as the cumulative quantity of time during which the machine’s engine has been running. This is generally the value of the hour meter on the machine.
- Other data points: Based on the AEMP Telematics Standard, ISO 15143-3, this API provides a wide range of other data points that might be of interest and an overview of all data points can be found in the sample response for the endpoint - e.g. idle hours, fuel level and usage, distance travelled.
Fetching data for a single asset
The single-element snapshot endpoint provides the snapshot of the latest available telematics data for a single equipment identified by the OEM ISO identifier parameter. The response format is the same as for the fleet snapshot endpoint.
Step 2: Optimizing API requests to avoid rate limit errors
Trackunit recommends fetching data from the ISO Export API once per day for ERP integrations to ensure efficient synchronization while minimizing unnecessary API requests.
The API is rate-limited to prevent excessive usage and ensure system stability. Specifically, requests to the API are limited to one request per URL every 15 minutes. Additionally, there are per-customer limits on request frequency across all API accounts associated with the same customer:
- Fleet snapshot pages: Maximum 50 requests per second
- Single-element snapshot endpoint: Maximum 500 requests per second
To avoid hitting rate limits, it is important to schedule data retrieval efficiently and implement retry logic when encountering rate limit errors.
Push rental ERP data from an ERP system into Trackunit
In modern fleet management, integrating rental ERP systems with telematics solutions like Trackunit is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and data consistency. Trackunit’s Rental API enables rental companies to seamlessly transfer key data—such as customers and contracts—from their Rental ERP system into Trackunit Manager, where users can monitor and manage their assets in real-time.
IrisX Subscription neededThe Rental ERP API is only available for IrisX enabled customers. Learn more about the IrisX subscription.
Step 1: Understand and map concepts and data
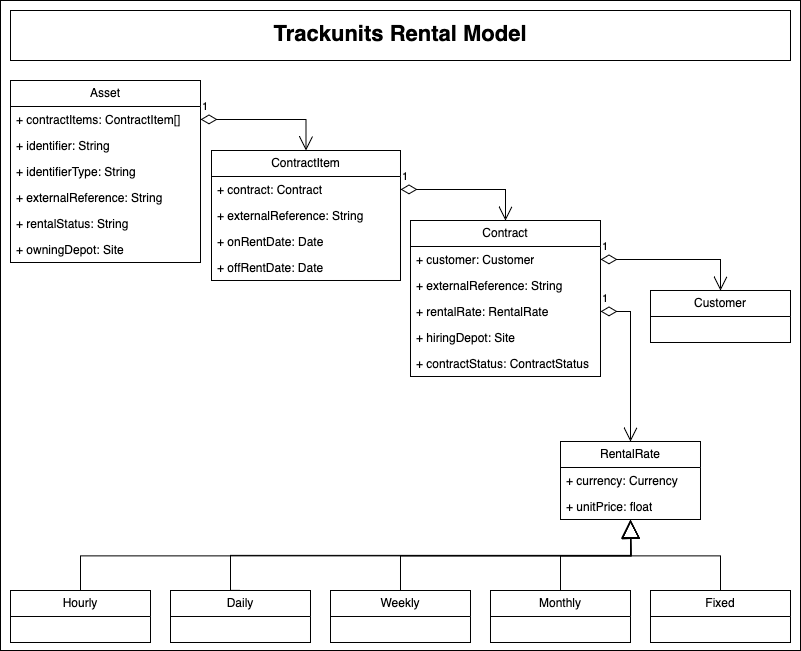
The Trackunit data model consists of the following concepts for rental ERP data:
Data points connected to an asset:
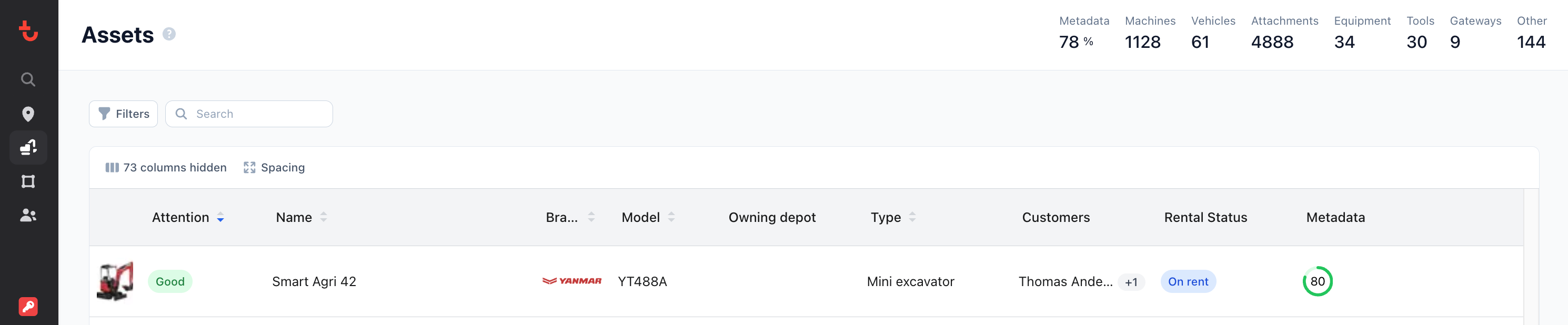
- Identifier Type: It is possible to match with asset in Trackunit Iris based on their asset id, serial number or external reference. This field combined with the identifier field is used when looking up an asset.
- Identifier: The identifier used for matching the asset that the contract information and rental status should be assigned to.
- Rental status: The rental status can be used to locate possible available assets accross all depots. Available types are :
- ON_RENT,
- PICK_UP_READY,
- AVAILABLE,
- RETURNED,
- IN_REPAIR,
- TRANSFER,
- OTHER,
- OFF_RENT,
- NOT_ON_CONTRACT,
- RESERVED.
- New types may be added.
- Owning depot: Depots created in Trackunit Iris can be linked to assets to have an overview of all assets on a depot level.
- ExternalReference represents an identifier from the ERP system and has to be unique.
Contracts
The contracts can be used for assigning an unassigning assets to and from customers which also makes them available in the customer portal. Contracts can have relations to many contract items, which hold details about specific rental periods.
- Associated customer
- External Reference to the contract in an external system, i.e., an identifier of the item. Must be unique.
- Contract status:
- OPEN
- RESERVED
- CANCELLED
- COMPLETED
- New values may be added.
- Start date and end date of the contract
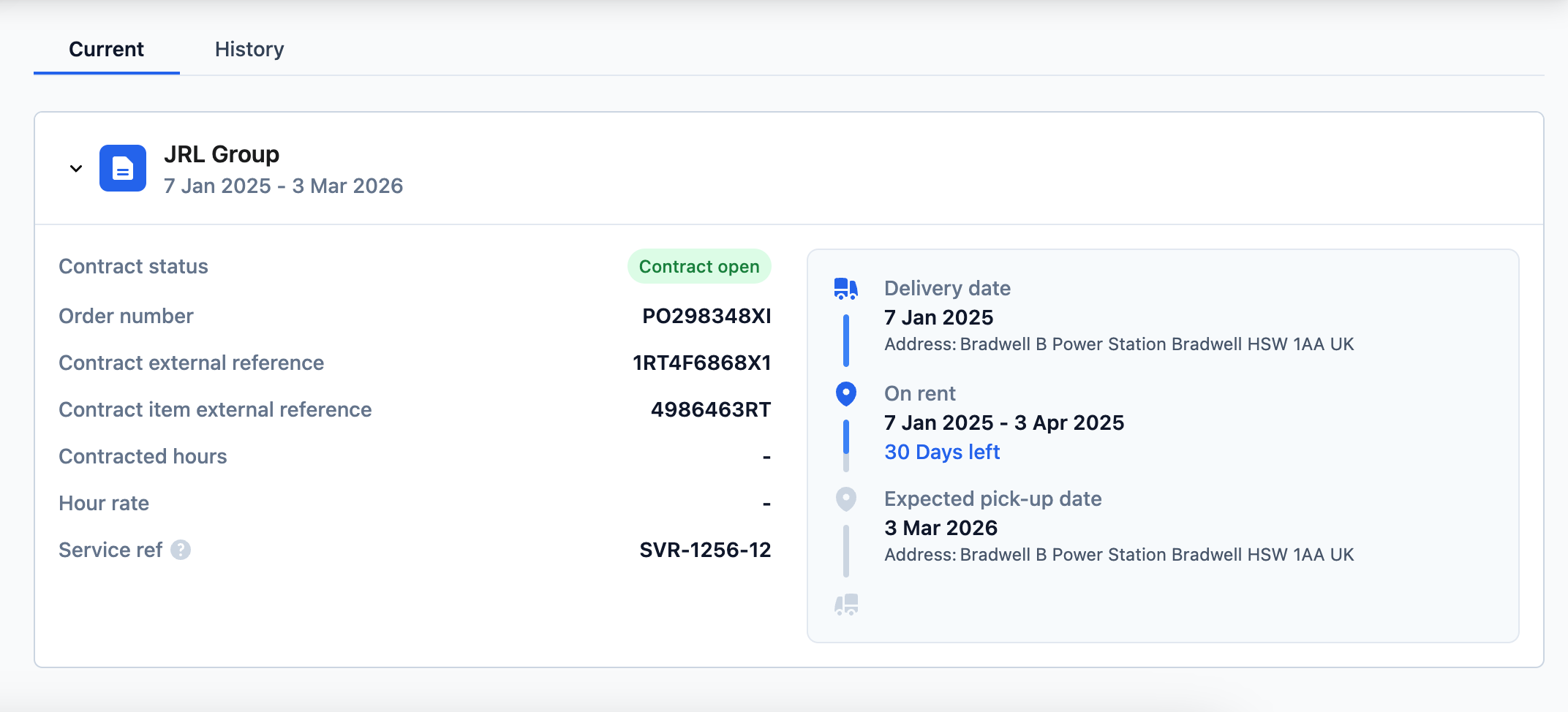
Data points connected to a contract item:
- Rental period: Determines when an asset should be available for a customer.
- OnRent Date
- OffRate Date
- Rental Rate: Rental rates can contain information about price for renting assets.
- Hiring depot: When sharing data about hiring depot as part of the rental contract your customers can get access to data about which depot has rented an asset to them.
- Delivery / pickup address: By sharing information about delivery/pickup address it will be possible to see where and when assets are expected to be delivered and/or picked up.
- Delivery / pickup date: share information about when the delivery and pickup of the asset can be expected.
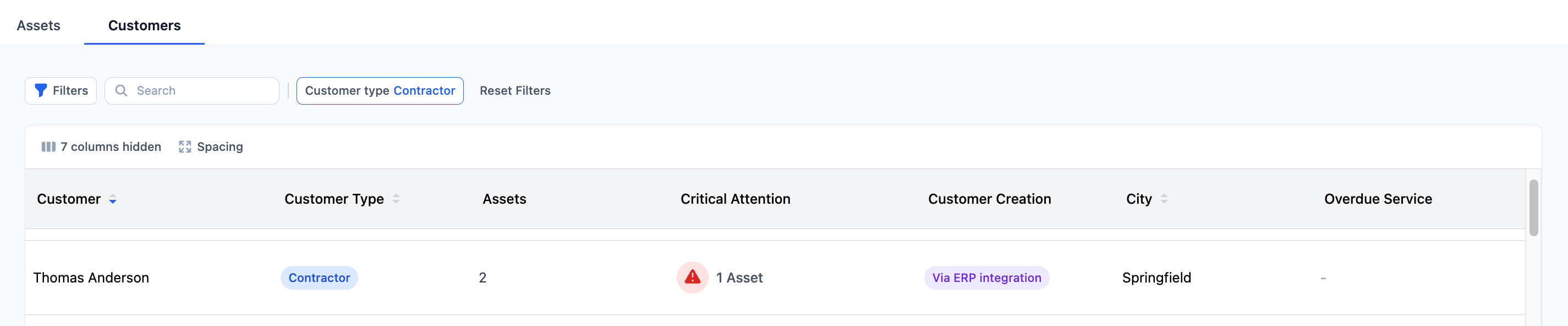
Customers
By providing data about customers you will be able to share data about the asset with customers through customer portals. The information about customers and the asset they have access to can also be used to filter assets and get an overview of what assets a customer has access to.
- externalReference: External identifier of the customer in the Iris platform
- Type of customer
- Contractor
- Dealer
- Distributor
- OEM
- Rental
- Service
- Other
NoteOnce the Rental API is enabled the Customer feature in Manager will no longer allow for manual creation or editing to preserve system integrity.
Step 2: Extending the data model for custom needs
Custom fields provide a way to define new fields in the Trackunit data model. Allowing to extend and customize Trackunit Manager. Currently we support extending the data model of assets, accounts, groups, sites, customers and rental contracts with new fields. Learn more in the Custom Fields API -Introduction.
Custom Field ExamplesSpecifically for rental contracts, you can think of custom fields to store any additional data that is not accounted for in Trackunit’s rental data model - for example: “customer project code” or “service reference”.
Step 3: Synchronizing ERP data via the Rental API
Preparation of data
- Get an overview of all available assets in Trackunit and their unique identifiers like asset ID and serial numbers (PIN / VIN etc) via the Asset API - get assets endpoint
- Prepare assets by setting ExternalReference via the Asset API - update asset endpoint
- If you wish to use the “owning depot” and “hiring depot” features, then use the Sites API to get all sites created in Trackunit and add new sites by using the create site endpoint. Remember to choose the type “depot”.
Synchronize ERP data
Use the Rental API - Synchronize rental data endpoint to start pushing rental ERP data to Trackunit. Data can be pushed for one asset per request.
If customers are updated through the Rental API and customers are not already created in Trackunit Iris, then they will automatically be created. Customers can also be created through the Customer API which allows you to control which customers are available on Trackunit Iris independently of rental contracts.
To have up to date information in Trackunit updates can be pushed to Trackunit as soon as they are registered in the ERP system as long as it stays within the configured rate limits.
Updated 5 months ago